Creating calculated and arbitrary waveforms
Usage:
vs = gr.vector_source_x ( data vector, bool repeat )
where x can be any of b, c, f, i, s for byte, complex, float, integer or short. set repeat to 1 to repeat, 0 to not repeat.
We can use gnuradio's vector_source to send a Python list of numbers. This list
can be calculated, read from a file, input from an audio source, anything.
Example
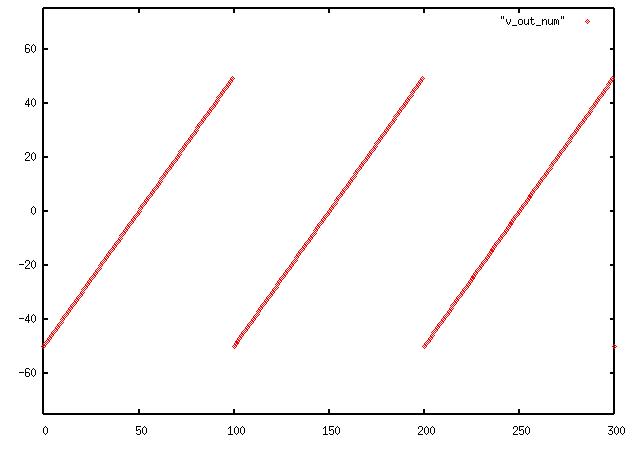
Let's create a simple ramp function from -50 to 50 and send it
out to a file:
v = range(-50,50)
fg = gr.flow_graph()
vsource = gr.vector_source_f (v, 1) # repeat
dst = gr.file_sink (gr.sizeof_float, "v_out")
fg.connect (vsource, dst)
Here is the output file v_out:
Example
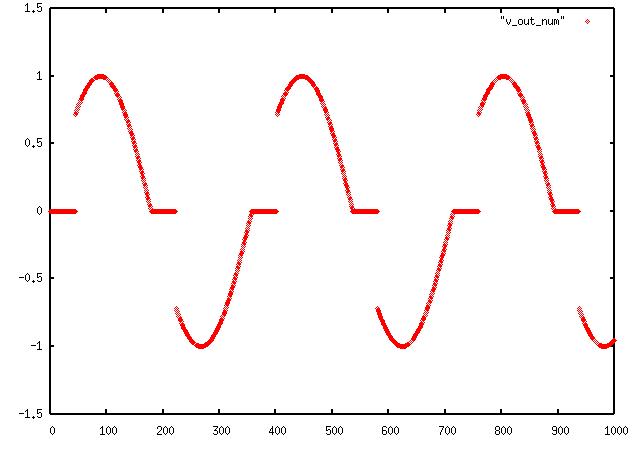
Next we will use a series of piecemeal functions to simulate the waveform of a triac firing at 45 and 225 degrees in a
sinewave like a light dimmer set at 3/4:
v = []
for a in range(0,45):
v = v + [0]
for a in range(46,180):
v = v + [ math.sin( a * ( 6.28/360 )) ]
for a in range(181,225):
v = v + [0]
for a in range(226,360):
v = v + [ math.sin( a * ( 6.28/360 )) ]
fg = gr.flow_graph ()
vsource = gr.vector_source_f (v, 1)
dst = gr.file_sink (gr.sizeof_float, "v_out")
fg.connect (vsource, dst)
produces this noisy wave: